Articles About Timekeeping (39)

AM and PM Explained
How does the 12-hour clock system work? Is midnight 12 am or 12 pm?

Daylight Saving Time (DST)
Why do many countries set the clocks back and forth an hour twice a year?

UTC: The World’s Time Standard
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) is the basis for civil time today. This 24-hour time standard is kept using highly precise atomic clocks combined with the Earth's rotation.

History of DST
History of Daylight Saving Time (DST). Why was Daylight Saving Time created, who invented it, and what is the point of having a time change every year?

1 Hour Ahead or Back?
Which way do the clocks go? "Spring forward or fall back" is just one way to remember which way set the clocks for Daylight Saving Time (DST).

UTC & GMT – Same Difference?
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is often interchanged or confused with Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). But GMT is a time zone and UTC is a time standard.

The Never-Ending DST Debate
Daylight Saving Time (DST) has been used for more than But do its pros really outweigh its cons?

GMT or BST in the UK?
The UK is not on Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) all year. During Daylight Saving Time the correct time zone is British Summer Time (BST).

What Is Standard Time?
Standard time is also known as winter time or normal time in some countries.

Transition to DST
When Daylight Saving Time (DST) starts, clocks go forward; when it ends, clocks go back. So what is Daylight Saving? Do we gain an hour or lose an hour?
What Is the International Date Line?
The International Date Line goes through the Pacific Ocean at about 180 degrees longitude. Where is the International Date Line? See it on a time zone map.

What Is a Time Zone?
A time zone refers to any region where the same standard time is kept. Interactive Time Zone Map for current time zones worldwide.

International Atomic Time
International Atomic Time (TAI) is one of the main components of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), the time scale used to determine local times around the world.

Daylight Savings or Saving?
“Daylight Saving Time” is the correct term, but “Daylight Savings Time” with an “s” is at least as commonly used.

When Did DST Start in Europe?
Daylight Saving Time (DST) was first adopted in Europe by Germany in 1916.

What Is Solar Noon?
Noon is at 12 o'clock but solar noon can be at a different time. What's the difference between the two?

Why Do We Have Time Zones?
The expansion of transport and communication during the 19th century created a need for a unified time-keeping system, and time zones were introduced.

Equation of Time
Time measured by the Sun is not the same as time measured by our clocks. The difference between the two is called the equation of time.

Summer Time or DST?
Summer time is often used to describe Daylight Saving Time (DST), especially the United Kingdom. Winter time instead of standard time is also a common variation.

What Is Universal Time?
Universal Time is a solar time standard used in astronomy and to define time on Earth. How is it measured? What's the difference between UT, UT0, UT1, UT2, and UTC?

How Long Is a Day on Earth?
In terms of solar time, most days are a little longer than 24 hours. Exact day length for today and yesterday.

Why UTC – not CUT?
The abbreviation for Coordinated Universal Time is UTC. Why is it not abbreviated as “CUT” or “TUC”?

Internet Time
What is Internet Time, and how to convert between the time zones and beats.
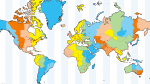
What Is a Time Zone?
The term time zone can be used to describe several different things.

How Does an Atomic Clock Work?
Atomic clocks are among the most accurate timekeepers in human history. Just how precise are they and how do they work?

What Is Local Mean Time?
Use a sundial to determine the time of day and you will probably be off by a few minutes. That's where LMT comes into play. How is it measured and what is it used for?

What Are Leap Seconds?
Every now and then a leap second is added to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) in order to synchronize clocks worldwide with the Earth's rotation.

Timekeeping by Stars
Out and about at night without a watch or a smartphone readily available? If you are in the Northern Hemisphere use the Big Dipper and the North Star to tell the time.

The Future of Leap Seconds
Organizations and individuals have for many years argued about abolishing leap seconds for good.

Alternative Time Systems
Astronomers use other measures of time, such as Terrestrial Time (TT), which is 32.184 seconds ahead of International Atomic Time (TAI).

Length of Tropical Years 1900–2100
Exact length down to the second of tropical years ranging from 1900 to 2100. It is also known as a solar year, astronomical year, or equinoctial year.

Earth Is Speeding Up
Our home planet has been spinning unusually fast lately. 2020 had some of the shortest days on record.

The Earth Keeps Good Time
While we are constantly trying to build a better clock, it’s easy to forget there’s a very accurate timekeeper right under our feet: planet Earth.

Military Time: The 24-Hour Clock
Military Time uses a 24-hour time format and the NATO alphabet. How does it work? Conversion chart: What is 1500 Zulu Time in 12-hour AM/PM format?

Will a Negative Leap Second Be Needed Soon?
Our planet is currently spinning, on average, ahead of schedule. This might lead to a negative leap second.

Winter Time Is the Same as Standard Time
Winter time is often used to describe the time of year when a country is not on Daylight Saving Time (DST). It is officially known as standard time.

Equation of Time
Why doesn't the year's earliest sunset occur on the winter solstice, even though it is the shortest day of the year in terms of daylight?

The End of the Leap Second?
A resolution passed on November 18, 2022, means the world may be moving closer to getting rid of leap of seconds.

Earth Sets New Record for Shortest Day
On June 29, 2022, Earth recorded its shortest day since scientists began using atomic clocks to measure its rotational speed.